How Long Until a Tooth Infection Kills You? Understanding the Risks and the Urgency
When tooth infections go untreated they can result in serious, life threatening complications. Although most of us don’t give much thought to a tooth infection. it’s a pretty serious affair and one that can quickly turn life threatening. Indeed in rare situations tooth infection can also lead to death. But how long does it actually take? How serious is the threat?
You may be surprised to learn that an untreated tooth infection can lead to sepsis which kills more than 250,000 people each year in the United States. Well this isn’t a tooth decay this is a toothache and that’s the mechanics of a toothache toothaches are your health and dental infections are something you should treat as soon as possible. So how long do you have before a tooth infection can kill you? So, let’s discuss this important subject in depth.
Introduction:
Dental health is something we often take for granted until something goes awry. A small cavity can lead to a serious infection and although it might seem annoying at first an untreated tooth infection can be a life threatening situation. You may ask, How long do I have if I leave a tooth infection untreated? The answer isn’t straightforward, but awareness of the risks is crucial for all.
A tooth infection happens when bacteria enter the tooth’s pulp (the soft tissue inside the tooth) or the surrounding tissues. If the infection is not treated it can spread to different parts of your body and cause serious complications. The infection can in rare instances also cause death. However thanks to modern dental care infections are very treatable and the risk of serious complications is low when treated promptly.
In this guide we’ll give you the lowdown on the timeline of tooth infection how it spreads and the information you need to respond quickly. We want to show you when it’s time to get medical care and how you can help prevent your tooth infection from becoming a much more dangerous event.
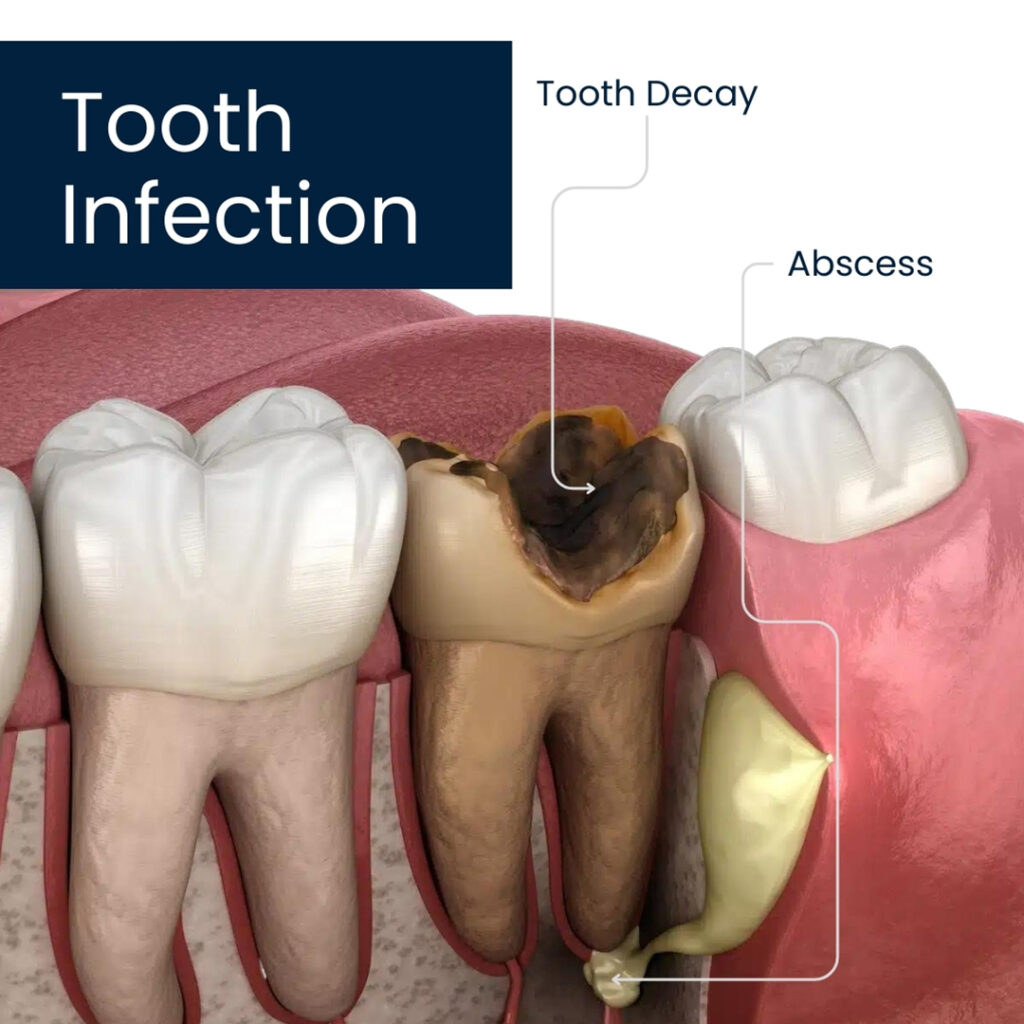
What is a Tooth Infection?
Before we get into how long after a tooth infection can be fatal. it’s important to know what a tooth infection is and how it forms. Tooth infections usually start with a cavity or damage to the tooth that leads to bacteria invading the inner pulp. The pulp, the soft tissue holding nerves and blood vessels is especially susceptible to infection.
Types of Infection:
Tooth abscesses fall into two chief categories:
- Periapical Abscess (Root Abscess): This type develops when bacteria enter the pulp of the tooth typically due to a cavity crack or chip. The infection can spread into the root leading to intense pain swelling and sometimes fever.
- Periodontal Abscess (Gum Abscess): This type of infection occurs in the gum tissue surrounding the tooth and is typically the result of untreated gum disease. It can lead to swelling redness and extreme pain where affected.
Both types of infections can be painful but they can also be serious if left untreated.

How Fast Can a Tooth Infection Get Dangerous?
With a tooth infection your body is working overtime to kill the bacteria that is the source of trouble. But if the disease isn’t treated it can progress beyond the tooth and into the tissues around it including the jaw face and neck and even your bloodstream. Occasionally untended to tooth infections can turn deadly in a matter of days to weeks.
The Timeline of a Tooth Infections:
The progression of a tooth infection varies depending on several factors including how severe the infection is where it is located and the speed of treatment. Here’s an approximate timeline of how a tooth infection could develop:
- Early Symptoms (0–2 days): During the very early stage of a tooth infection, you may have mild symptoms that include a toothache sensitivity to hot/cold or tenderness in the area. Initially you may notice swelling and redness around the tooth or gums but the infection remains localized and treatable at this time.
- Facial and Jaw Infections (3-5 Days): If not treated the infection can spread to surrounding tissues leading to more severe symptoms. You might also experience more swelling a fever that doesn’t go away and trouble opening your mouth or swallowing. The pain can increase and drainage of pus can leave a bad taste in your mouth. At this point the infection may be spreading to the jawbone or neighboring tissues and timely dental treatment is crucial.
- Brain Infection (Brain Abscess) (6-10 days): If the infection continues to spread it may involve deeper tissue even bone and complete an abscess. The swelling may spread beyond the gums to include the face and neck. You start wanting to lay down you get vomiting or shaking chills. If left untreated the infection could spread more, possibly going into your blood.
- Heart Infection (Endocarditis) (11-14 Days or More): An untreated tooth infection may pose life threatening complications if it lasts 2 weeks or longer most notably sepsis that is an infection that spreads throughout the body. Sepsis can lead to organ failure and is frequently life threatening if not treated promptly. Another potential complication Landers said is if the infection spreads to the brain heart or lungs which could cause serious overall problems or death.

How Does a Tooth Infection Work Its Way to the Whole Body?
A tooth infection may extend to other parts of the body in multiple ways thus having the danger of causing life threatening diseases. Here’s how it can happen:
- Blood Infection (Sepsis): When the infection pushes through from a tooth into adjacent tissues it could eventually reach the bloodstream resulting in sepsis. Sepsis a severe and potentially life threatening illness can cause organ failure shock and death without prompt treatment. More than 250,000 Americans die from sepsis each year according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) and untreated infections are a key factor.
- Facial and Jaw Infections: Infection of the jawbone or abscess associated with the face can result in a condition called cellulitis a serious soft tissue infection. This can also result in Ludwig’s Angina in some cases which is a dangerous type of neck and mouth infection that may block breathing and cause suffocation.
- Brain Infection (Brain Abscess):This is a rare occurrence and happens when bacteria from an infected tooth spread to other body parts through the bloodstream and into the brain causing a brain abscess. This is a rather severe condition that can result in neurological injury or death without quick medical consideration.
- Heart Infection (Endocarditis): The bacteria from an infected tooth can also enter the bloodstream and reach the heart especially if you have certain underlying conditions such as heart disease or a weakened immune system. An infection of the heart valves called endocarditis can set in sometimes leading to heart failure stroke or death.

The Risk Factors That Affect the Severity of a Tooth Infection:
Not every person faces the same risk when it comes to tooth infections. Several factors can determine how quickly a tooth infection can become dangerous and how likely it is to cause complications:
- Immune System Health: Individuals with weakened immune systems (like those with diabetes and HIV/AIDS or cancer) are more vulnerable to infections spreading rapidly.
- Age: The very young and the elderly might struggle to fight off infections increasing the risk of complications.
- Dental Hygiene: Lack of dental hygiene and avoiding dental checkups can cause infections.
- Underlying Health Conditions: Having diseases like heart disease or diabetes can raise the risk of complications like heart infections or sepsis.
- Delay: The longer you put off getting a tooth infection treated the more likely it is to spread and lead to life threatening complications.

What to Do if You Suspect You Have a Tooth Infection:
If you believe that you have a tooth infection it’s crucial to take swift action. Here are the steps you ought to follow:
- Get Immediate Dental Care: Visit your dentist immediately if you’re having pain swelling fever or discomfort. A dentist can identify the infection and suggest a suitable treatment option.
- Follow Treatment Plans: In most situations a dentist will need to treat the infection with antibiotics or perform some other procedure such as a root canal or tooth extraction to eliminate the source of the infection.
- Monitor Symptoms: If your symptoms get worse or you develop new symptoms such as shortness of breath extreme fatigue or confusion go to a doctor immediately.
- Do Not Delay: Postponing treatment can cause the infection to spread faster increasing the risk of severe complications.
Key Takeaways:
- Common but serious tooth infections can lead to life threatening complications if not treated.
- A tooth infection can travel from the tooth into surrounding tissues and get into the bloodstream resulting in sepsis and other fatal conditions.
- Tooth infection progression can vary from one case to the next but it tends to increase risk the longer treatment is delayed.
- Early intervention is critical in avoiding complications and achieving a full recovery.
FAQs
1. How long can a tooth infection go untreated before it kills you?
If left untreated a tooth infection can be deadly within 1-2 weeks, depending on how quickly it spreads.
2. Are there ways to treat a tooth infection at home?
At home remedies may relieve some symptoms temporarily but you need to see a dentist for professional care as soon as possible.
3. How can I tell if tooth infection has spread?
Symptoms such as severe swelling fever, breathing difficulty or profound fatigue might mean the infection has spread.
4. Can tooth infection kill you?
Yes untreated tooth infections can have serious fatal complications in rare cases such as sepsis or brain abscesses.
5. Do antibiotics treat a tooth infection?
Antibiotics can help control the infection to some extent but the underlying source of the infection (like a cavity or abscess) usually needs to be addressed via dental work.
6. How is a tooth infection treated?
Treatment generally includes antibiotics and draining any abscesses, and potentially a root canal or extraction to remove the infected tissue.
Conclusion:
Though it’s uncommon an untreated tooth infection can be fatal. THK Tooth infections should not be taken lightly and medical attention should be sought immediately. The sooner you get treatment for the infection the less likely you are to face serious complications. Always practice good oral hygiene have regular dental checkups and pay attention to your body if something doesn’t feel right something is probably not right.
Knowing the risks and being proactive can keep us from having the things we love come back to kill us. Be healthy and do not wait your teeth (and your life) are at stake.