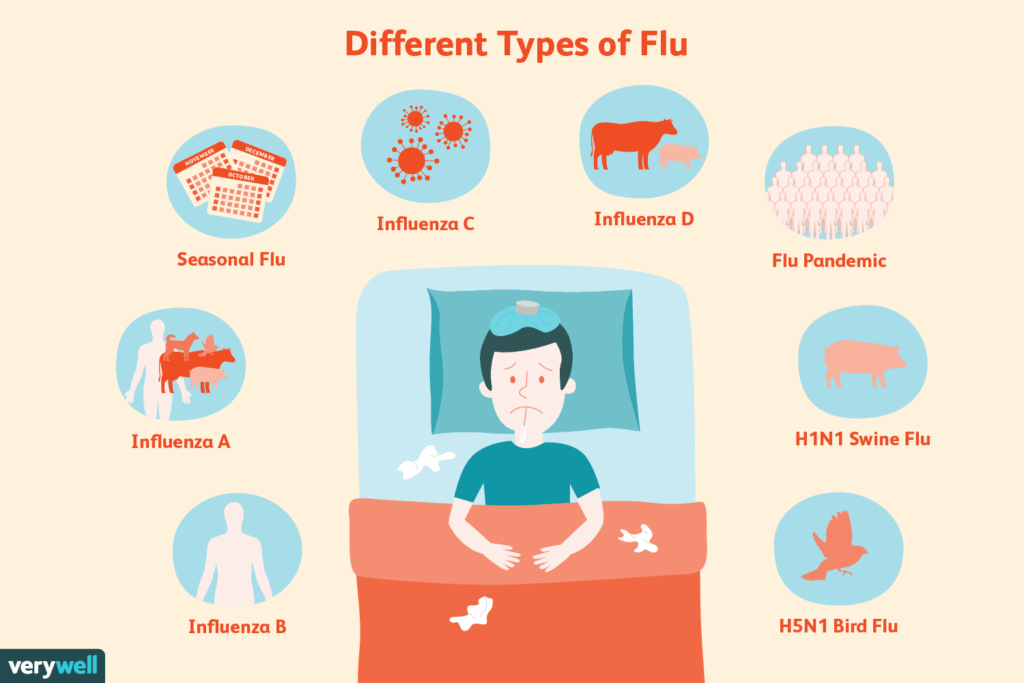
Introduction: How Many Deaths From the Flu?
Fortuitously did you know that your average flu season leads to more than 200,000 hospitalizations every year in the U.S alone? It’s a staggering number and what is even more surprising is that influenza viruses technically called Flu A vs. Flu B is what is putting people in the hospital and causing death. But what exactly are the differences between these two strains of the flu and why should we care?
In this article we’ll take a closer look at the main differences between Flu A and Flu B their effects on our health and what we can do to stay safe during flu season. Whether you’ve faced the flu before or simply want to be armed with knowledge we’ll walk you through everything you need to know. So let’s do a deep dive into the world of Flu A vs Flu B.
What is the Flu Really?
Before we dive into what exactly Flu A and Flu B are let’s take a step back and talk about the flu virus itself. Flu is caused by the influenza virus which has several types. The most usual ones which affect people are:
- Influenza A
- Influenza B
- Influenza C (rarely infects humans)
Flu A and Flu B cause seasonal outbreaks of the flu but Flu A is more often the dominant virus in many flu seasons. But Flu B does contribute to infections too especially among kids.

What’s the Difference Between Flu A and Flu B?
Flu A and Flu B (no they aren’t a band) may seem pretty similar at first blush they both lead to fever fatigue cough and aches and pains. But as we dig in deeper we will uncover some major differences between the two of them.
1. Type of Virus
- Flu A is the more adaptable of the two. It can infect both human and animal (especially birds) hosts. This means it can spark seasonal outbreaks even pandemics.
- Flu B however is more restricted and infects only humans. It tends to cause less severe outbreaks than Flu A though it can also result in serious complications.
2. Severity of Illness
- Flu A usually causes more serious disease. It is notorious for causing global outbreaks and even pandemics. Certain strains of Flu A particularly the H1N1 subtype have previously led to global flu pandemics such as the swine flu epidemic in 2009.
- Flu B is usually less severe than Flu A but it can still cause serious illness particularly in children and the elderly.
3. Mutations and Variants
- Flu A has a higher mutation rate resulting in new strains of the virus. This is the explanation behind the different subtypes of Flu A (H1N1 or H3N2) we observe every season. This constant change makes it more difficult to predict precisely which strain will circulate in a given flu season which is why the flu vaccine is updated annually.
- Flu B is thought to be less unpredictable is that it mutates less frequently than Flu A. But it still can generate new strains that challenge public health.
4. Impact on the Population
- Flu A is more prone to cause widespread illness especially among young adults and the elderly. It’s responsible for the majority of the severe flu cases and hospitalizations.
- Flu B primarily circulates among children and usually results in milder symptoms however it can still cause severe complications such as pneumonia in at risk groups.

How Does Flu A and Flu B Spread?
Flu A and Flu B are both highly contagious viruses that are spread most often via droplets from a person’s cough sneeze or talk. They can also live on surfaces for a short period so you can easily catch the virus by touching an infected object and then your face.
To add to the risk people with Flu A or Flu B can start infecting others before any symptoms have appeared making it particularly insidious to try to get a handle on its spread.
Flu symptoms: How to tell the difference?
Flu A and Flu B symptoms may be quite similar though there are some key differences:
A and B have this flu symptoms in common:
- Fever or chills
- Cough
- Sore throat
- Runny or stuffy nose
- Muscle or body aches
- Fatigue
Key Differences:
- Flu A: Symptoms tend to be more intense with higher fevers and more profound fatigue. You might also feel greater body aches and chills.
- Flu B: The symptoms tend to be milder and can be more localized. For example you may experience more congestion or a sore throat without the painful body aches that typically accompany Flu A.
Vaccines: Are They Effective for Both Types?
Yes flu vaccines protect against both Flu A and Flu B but because the flu virus is constantly changing the vaccine must be updated every year to include the strains that are most likely to circulate during flu season.
The flu vaccine usually contains protection from these:
- Flu A (H1N1)
- Flu A (H3N2)
- Flu B (Victoria lineage)
- Flu B (Yamagata lineage)
The vaccine isn’t 100 percent effective but is the best way to lower your risk of becoming sick. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) advise that everyone aged 6 months and older be vaccinated yearly.
Preventing Flu A and Flu B
Here are some evidence informed strategies for reducing your chances of contracting the flu:
- Wash your hands often: With soap and water scrubbing for at least 20 seconds.
- Cover your coughs and sneezes: Always do so with a tissue or your elbow to avoid spreading germs.
- Avoid close contact with sick people: If it’s known that someone is sick maintain a safe distance.
- Stay home if you’re sick: Get plenty of rest and avoid spreading the virus to others.
What to Do if You Get the Flu
If you think you might have the flu however it’s important to get medical advice. Most people will recover from the flu in a week or two but some individuals may require antiviral medications especially if they are at increased risk of complications.
Here’s what you can do:
- Rest: Allow your body to return to a state of healing.
- Stay hydrated: Drink plenty of fluids to help with fever and congestion.
- Take over the counter medicine: Medications such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen may ease a fever and aches but be sure to follow dosage recommendations.
If you’re at higher risk (such as being pregnant elderly or having a chronic health condition) antiviral treatments such as oseltamivir (Tamiflu) may be prescribed to help shorten the duration of illness and prevent complications.
Key Takeaways
- Both viruses belong to the influenza genus, and Flu A is generally more serious and causes big outbreaks including pandemics Flu B is less common and usually milder.
- Flu A and Flu B spread easily and have the same symptoms in their early stages but Flu A is usually more severe.
- Vaccination is key to preventing both types of the flu with good hand hygiene and avoiding close contact with those who are sick being important steps for prevention.
- If you do get the flu your best bet is rest hydration and if needed a call to your health care professional.
Frequently Asked Questions About Flu A vs Flu B
1. Can I catch the flu from the flu vaccine?
No the flu vaccine is made from an inactivated virus or a weakened virus it cannot give you the flu. Some people might have mild side effects such as a sore arm but these are not the flu.
2. How long does the flu last?
Symptoms of the flu can last from 3 to 7 days though people may still feel exhausted for weeks afterward.
3. Does Flu A and Flu B get treated differently?
Treatment is similar for both types of flu rest, fluids, and antiviral medications if prescribed by a doctor.
4. Every year why do we need a new flu vaccine?
The flu virus evolves constantly which means the vaccine must be refreshed every year to be effective against the most common strains.
5. Is it possible for me to get both Flu A and Flu B in one season?
Yes you can be infected with both Flu A and Flu B in the same flu season not often but it can happen.
6. Are Flu A and Flu B contagious before symptoms present?
Yes Flu A and Flu B both can be transmitted by infected people even before they have signs of illness.
This is a conclusion of the article Stay Prepared Stay Safe
Flu A and Flu B are important and different in some key ways but one thing seems very clear. Both are serious threats to health and we all have to take them seriously. If we’re aware of the way that these viruses spread how to recognize their symptoms and vigilant with our prevention methods we can also help protect ourselves and those around us from the flu.
As always the best way to protect ourselves from the flu is with the annual flu vaccine and we can reduce our risk of getting or spreading the virus by taking simple precautions such as frequent handwashing covering our coughs and staying home when ill.
Get the latest flu and Covid news Stay Well And Keep Up with Flue season Ahead!